OFDMA Symbol Structure and Sub-Channelization


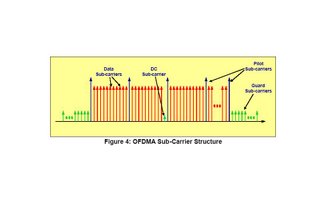
The OFDMA symbol structure consists of three types of sub-carriers as shown in Figure
4:
Data sub-carriers for data transmission
Pilot sub-carriers for estimation and synchronization purposes
Null sub-carriers for no transmission; used for guard bands and DC carriers
Active (data and pilot) sub-carriers are grouped into subsets of sub-carriers called subchannels.
The WiMAX OFDMA PHY [3] supports sub-channelization in both DL and
UL. The minimum frequency-time resource unit of sub-channelization is one slot, which
is equal to 48 data tones (sub-carriers).
There are two types of sub-carrier permutations for sub-channelization; diversity and
contiguous. The diversity permutation draws sub-carriers pseudo-randomly to form a
sub-channel. It provides frequency diversity and inter-cell interference averaging. The
diversity permutations include DL FUSC (Fully Used Sub-Carrier), DL PUSC (Partially
Used Sub-Carrier) and UL PUSC and additional optional permutations. With DL PUSC,
for each pair of OFDM symbols, the available or usable sub-carriers are grouped into
clusters containing 14 contiguous sub-carriers per symbol, with pilot and data allocations
in each cluster in the even and odd symbols as shown in Figure 5.
A re-arranging scheme is used to form groups of clusters such that each group is made up
of clusters that are distributed throughout the sub-carrier space. A sub-channel in a group
contains two (2) clusters and is comprised of 48 data sub-carriers and eight (8) pilot subcarriers.
Analogous to the cluster structure for DL, a tile structure is defined for the UL PUSC
whose format is shown in Figure 6.
The available sub-carrier space is split into tiles and six (6) tiles, chosen from across the
entire spectrum by means of a re-arranging/permutation scheme, are grouped together to
form a slot. The slot is comprised of 48 data sub-carriers and 24 pilot sub-carriers in 3
OFDM symbols.
The contiguous permutation groups a block of contiguous sub-carriers to form a subchannel.
The contiguous permutations include DL AMC and UL AMC, and have the
same structure. A bin consists of 9 contiguous sub-carriers in a symbol, with 8 assigned
for data and one assigned for a pilot. A slot in AMC is defined as a collection of bins of
the type (N x M = 6), where N is the number of contiguous bins and M is the number of
contiguous symbols. Thus the allowed combinations are [(6 bins, 1 symbol), (3 bins, 2
symbols), (2 bins, 3 symbols), (1 bin, 6 symbols)]. AMC permutation enables multi-user
diversity by choosing the sub-channel with the best frequency response.
In general, diversity sub-carrier permutations perform well in mobile applications while
contiguous sub-carrier permutations are well suited for fixed, portable, or low mobility
environments. These options enable the system designer to trade-off mobility for
throughput.
0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home